ZQ Robotics: Disruptive Linear Joint Design
As technology advances rapidly, humanoid robots are transitioning from science fiction to reality, with expanding application domains. However, developing a robot that is both flexible, powerful, and anthropomorphic requires overcoming significant technical challenges in its core components—joint actuators. Particularly in areas like arms and legs, where high explosive power and compact size are critical, integrating robust power, transmission, and sensing systems within limited space remains a hurdle for researchers. Recently, a patent filed by Shenzhen ZQ Robotics Technology Co., Ltd.(Application Publication No.: CN 120038785 A) titled “A Linear Joint for Humanoid Robots and Humanoid Robot” reveals an innovative solution. Through highly integrated design, this patent aims to reduce the axial dimension of linear joints, making the robot’s “skeleton” more compact and its form more human – like.
Technical Bottlenecks in Current Humanoid Robot Joints
Before delving into this innovation, it’s essential to understand the problems it addresses. According to the patent, current mainstream electric – driven linear joints, despite their wide use, suffer from several core issues:
1.Low Integration, Bulky Structure: Existing joints typically combine multiple discrete components (e.g., motors, lead screws, push rods, force sensors, and rod – end bearings), requiring additional connectors and fasteners. This “patchwork” design leads to inefficiencies.
2.Excessive Axial Length: Cumulative components result in oversized joints along the axial direction, which is problematic for space – constrained areas like robot forearms.
3.Compromised Aesthetics and Practicality: Poor integration forces designers to compromise between “performance” and “appearance,” either lengthening robot limbs or exposing joint structures, thus undermining anthropomorphic aesthetics and functionality.
Core Innovations: Integration and Compact Design
The patent’s core lies in “integrated modularity”, which optimizes joint structure by consolidating functions into single components.
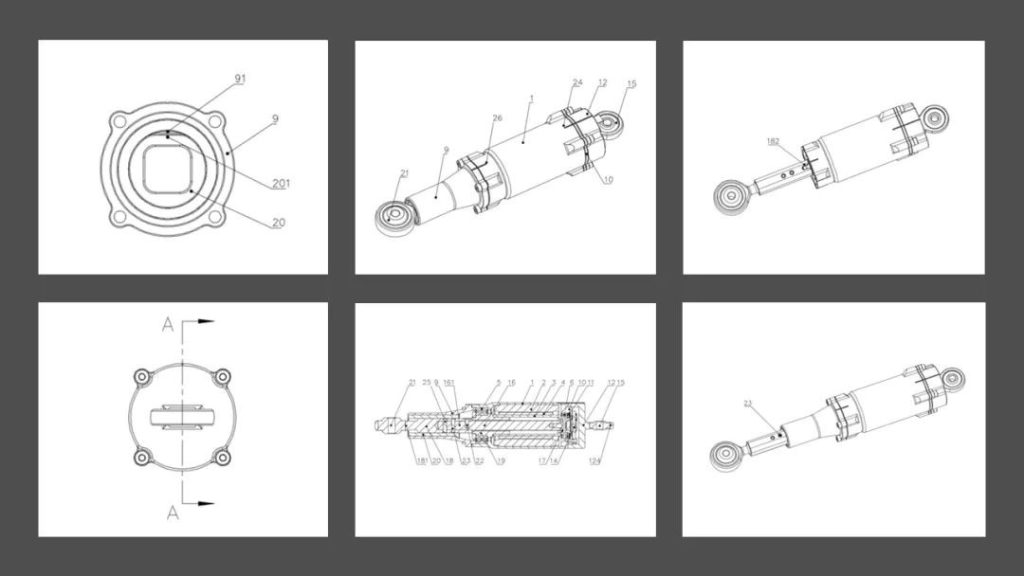
Innovation 1: Integrated Joint Bearing Housing
The most significant breakthrough involves integrating bearing housings directly with push rods and force sensors:
•Output End: The “output – end joint bearing housing” is integrated with the push rod assembly.
•Fixed End: The “fixed – end joint bearing housing” is integrated with the force sensor.
This allows bearings to be pressed directly onto the push rod and sensor structures, eliminating fasteners and reducing axial space.
Patent Quote: “The push rod assembly is integrally formed with the output – end bearing housing… The force sensor is integrally formed with the fixed – end bearing housing…”
Innovation 2: Compact Hollow Motor with Embedded Transmission
A hollow motor design further compresses space:
•The motor’s rotating part (rolling element) features a hollow cavity.
•The ball screw pair (core transmission mechanism) is placed inside this cavity, creating a “motor – in – screw” arrangement that overlaps power and transmission systems, shortening the joint length.
Patent Quote: “The rolling element contains an internal cavity for housing the ball screw pair.”
Innovation 3: Precise Anti – Rotation and Guidance Mechanism
To ensure linear motion (no rotation), a square – shaped “limit sleeve” is placed between the push rod and front cover:
•The sleeve’s inner surface matches the push rod’s square contour, physically restricting rotation.
•External flat surfaces on the sleeve align with positioning bosses on the front cover, ensuring accurate assembly.
Patent Quote: “The limit sleeve’s inner surface is square… corresponding to the push rod’s outer contour…”
Innovation 4: Assembly Alignment Marks
Precision assembly is ensured through alignment marks (first and second alignment marks) on the joint housing, end covers, and sensors. Workers align these marks to guarantee correct part orientation, improving efficiency and consistency.
Patent Quote: “The joint housing, rear cover, and force sensor are marked with first alignment marks… The front cover and housing have second alignment marks corresponding to the first alignment marks.”
Technical Advantages: Empowering Next – Generation Humanoids
These innovations translate into tangible benefits:
1.Compact Structure: Integration reduces parts and axial length, enabling sleeker, more human – like designs.
Patent Quote: “This design shortens the joint’s axial dimension, facilitating miniaturization and anthropomorphic design.”
2.Simplified Assembly: Fewer components and direct press – fitting eliminate complex fastening steps, lowering production costs and failure risks, ideal for mass manufacturing.
Patent Quote: “Direct bearing press – fitting reduces parts and assembly difficulty, supporting large – scale production.”
Conclusion
ZQ Robotics’ patent solves critical issues in humanoid linear joints through integration of bearing housings with push rods and sensors, complemented by a hollow motor, embedded transmission, and anti – rotation mechanisms. This technology not only enables more compact and aesthetically pleasing robots but also streamlines mass production, significantly advancing the humanoid robotics industry.
Patent Drawings

Active Community Global, Inc (ACG EVENTS Global) is a leader in conference planning and production. We produce world-class conferences like summits, technical forums, awards ceremony, company visiting and so on, focusing on areas of most relevance to our served industry sectors. We are dedicated to deliver high-quality, informative and value added strategic business conferences where audience members, speakers, and sponsors can transform their business, develop key industry contacts and walk away with new resources.